Are you having trouble making good welds on your sheet metal projects? Whether you’re working in automotive, aerospace, or electronics, knowing the right welding techniques is critical. Bad welds can cause your products to fail, and that means lost money. But don’t worry, I’m here to help you learn about the best welding methods and how to make your welding even better.
The best ways to weld sheet metal include MIG welding, TIG welding, spot welding, seam welding, tack welding, and stitch welding. To make your welding better, you need to choose the right method, get your metal ready to go, and control your heat input.
Welding sheet metal can be a challenge, especially when you’re working with thin materials that like to warp and distort. Picking the right welding method for your project is the key to making strong, long-lasting welds. Using the best practices for preparation and technique will make your welding better and help you get the quality you’re looking for.

What Are the Best Welding Methods for Sheet Metal?
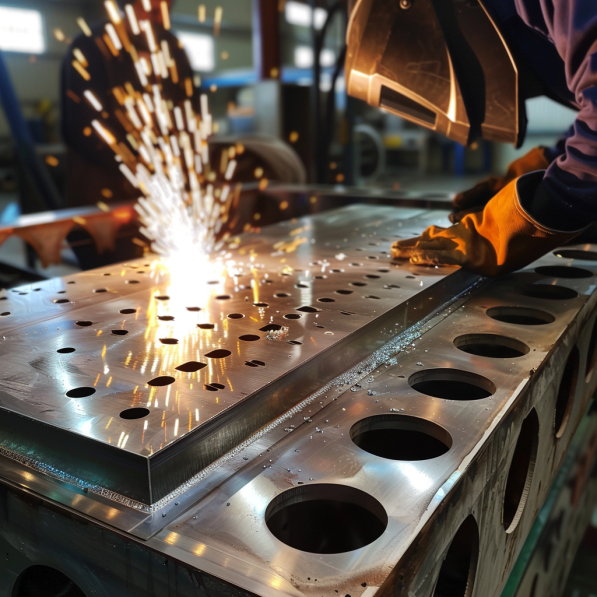
1.MIG Welding
MIG welding is one of the most popular ways to weld sheet metal because it’s versatile and easy to use. You have a welding gun that feeds a continuous wire electrode. The wire melts and fuses the pieces of metal together. MIG welding is great for thicker sheet metal. It makes strong, clean welds with low splatter. The automotive industry uses MIG welding a lot for body panels and frames.
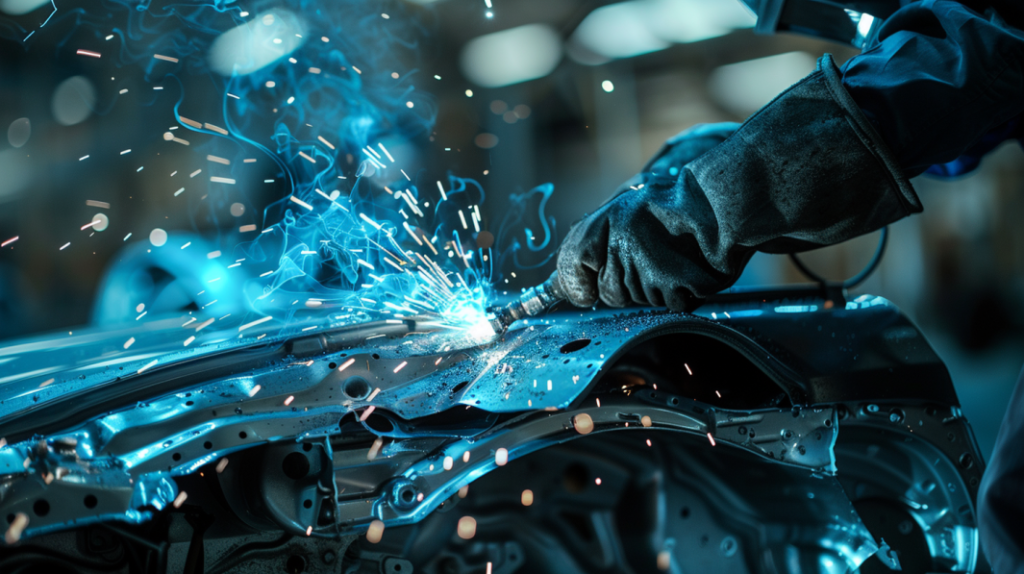

2.TIG Welding
TIG welding is known for its precision and control. It’s perfect for thin sheet metal and decorative welds. You have a tungsten electrode that’s not consumed. You use a separate filler rod to make the weld. TIG welding produces high-quality, great-looking welds with low distortion. It’s used a lot in the aerospace industry and for medical devices where you need precise, clean welds.
3.Spot Welding
Spot welding is a resistance welding method. It joins two or more sheets of metal by applying pressure and passing an electric current through the contact point. It’s great for joining thin sheet metal. You see it a lot in mass production, like in the automotive industry. It’s great for making strong, local welds without putting a lot of heat into the metal.
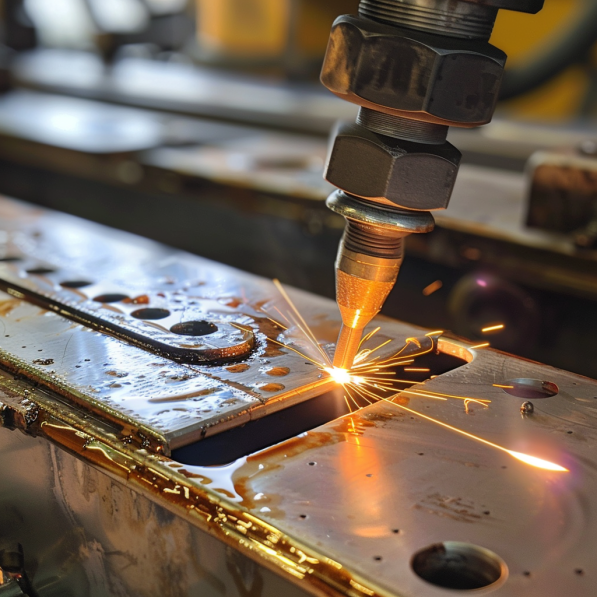

4.Seam Welding
Similar to spot welding, seam welding creates a continuous weld along a seam. You use wheel-shaped electrodes that roll along the metal surfaces. They apply pressure and electrical current to create a continuous, airtight, watertight joint. Seam welding is used a lot in the production of fuel tanks, exhaust systems, and other applications where you need to make a leak-proof seal.
5.Tack Welding
Tack welding is when you make temporary welds to hold the metal pieces in place before you make the final welds. You have to do this to make sure everything lines up and stays put while you’re welding. Tack welds are small and spaced apart. This allows you to make adjustments and keeps heat distortion to a minimum. Tack welding is important when you’re dealing with complex assemblies and when you need to make sure everything is in the right spot.
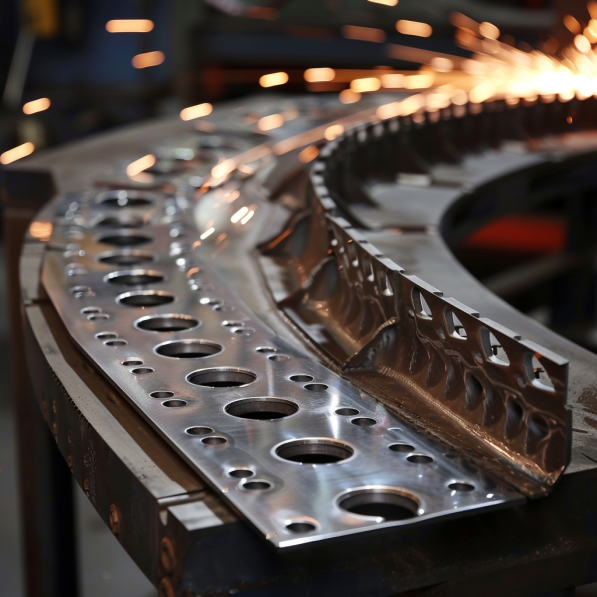

6.Stitch Welding
Stitch welding is when you make a bunch of small welds along the joint. You leave gaps between the welds. This helps keep you from putting too much heat into the metal and prevents it from warping and distorting. Stitch welding is useful when you don’t need to make a continuous weld and when you need to make sure the metal stays straight.

How Can You Optimize Your Welding Process?
- Choose the Right Welding Method
- The first step to making your welding better is to choose the right welding method for your project. You need to consider how thick the sheet metal is, how strong you need the weld to be, and what you’re going to use the part for. For example, TIG welding is great for doing precision work, while MIG welding works well for thicker materials and when you need to make a lot of parts fast.
- Clean the Metal Surface
- The next step in making your welding better is to clean the metal. You need to get all the dirt, grease, rust, and other junk off the metal. If you don’t, it will weaken your weld. Use a wire brush, grinder, or chemical cleaner to make sure the metal is clean and ready to weld.

- Use the Right Filler Metal
- The final step in making your welding better is to use the right filler metal. It needs to work with the base metal. The filler metal needs to be the same as the metal you’re welding to make sure your weld is strong and sticks together. For example, use aluminum filler rod to weld aluminum sheets and stainless steel filler rod to weld stainless steel sheets.
- Control Heat Input
- Controlling the heat is important to keep thin sheet metal from warping and distorting. You need to turn the heat down and move quickly along the weld joint to keep from building up too much heat. For MIG and TIG welding, you can control the heat by adjusting the amperage and how fast you move the torch along the joint. This will help you make a good, strong weld.
- Prepare the Joint Properly
- You need to prepare the joint properly to make sure the pieces fit together well and you get good welds. Make sure the pieces are lined up right and fit together tightly. Use clamps and fixtures to hold the pieces together while you’re welding. If you’re welding thicker sheets, bevel the edges so you have a V-groove. This will help you get good penetration and make a strong weld.
- Weld at the Right Speed
- The speed at which you weld affects the quality and strength of your weld. Welding too fast can make weak, incomplete welds. Welding too slow can build up too much heat and make the metal warp. Practice welding at a consistent, moderate speed to make sure you get a good, strong weld.
- Use Clamps and Fixtures
- You need clamps and fixtures to hold the metal pieces together while you’re welding. Clamps and fixtures keep the pieces from moving and make sure they’re lined up right. This is important for making sure you get a good, strong weld. Get good clamps and fixtures that can handle the heat and pressure of welding.

- Make Sure You Have Good Ventilation
- Welding produces fumes and gases that are bad for you. You need to make sure you have good ventilation in your workspace to get rid of these fumes and keep yourself safe. Use exhaust fans, ventilation systems, or weld outside to keep yourself from breathing in bad gases.
- Inspect Welds Regularly
- Check your welds to make sure everything is good. Look at your welds to make sure they’re good and that you don’t need to make any changes. Use dye penetrant or ultrasonic testing to make sure your welds are strong and don’t have any cracks or hole.
- Wear the Right Gear
- Welding makes a lot of heat, light, and sparks. You can get hurt bad if you’re not careful. You need to wear the right gear to keep yourself safe. Make sure you have a welding helmet with the right shade, flame-resistant gloves, long sleeves, and safety glasses. You need to protect yourself from burns, eye problems, and breathing in bad fumes.

- Understand Material Properties
- Different metals act differently when you weld them. You need to know how hot the metals get, how fast they conduct heat, and how much they expand when you weld them. This information will help you change your welding technique to make the best welds.
- Utilize Post-Weld Treatments
- You can do stuff after you weld to make your welds better. Heat treating, stress relieving, or cleaning up the weld can make your welds better. Doing stuff after you weld can get rid of the heat left in the metal, make the weld stronger, and make it look better. Do stuff after you weld based on what you need for your project.
How to Choose the Right Welding Method for Your Project?
Evaluate Metal Thickness
You need to pick the right welding method based on how thick the sheet metal is. For example, MIG welding is great for thicker sheets because it penetrates deep, while TIG welding is great for thin sheets because it’s precise.

Think About How Strong the Weld Needs to Be and How It Needs to Look
The strength of your weld and how it looks are important. TIG welding gives you good-looking, high-quality welds with low spatter, making it great for projects where the weld needs to look good. MIG welding makes strong welds fast, making it great for projects where the weld needs to be strong.
Analyze Production Volume
The welding method you choose may also depend on how many of the parts you need to make. For example, spot and seam welding are efficient and consistent when you need to make a lot of parts at once, while MIG and TIG welding are good for custom, one-off projects.

Advanced Techniques and Tips for Sheet Metal Welding
Preheat Treatment
Heating the metal before you weld it can help keep it from cracking, especially if it’s thick. This is super important when you’re welding metals that conduct heat really well, like aluminum and copper.
Use Backing Bars
Backing bars or backup strips help support the metal while you weld, especially when you’re working with thin sheets. They keep you from burning through and help you get a good, strong weld.
Pulse Welding
Pulse welding is when you alternate the welding current between a high peak and a low background current. This helps you put less heat into the metal, keep it from warping, and make good, strong welds. It’s really good for welding thin metals and metals that like to warp.
Hot and Cold Wire Feed
In TIG welding, you can use hot and cold wire feed techniques to make your welding better. Hot wire feed heats up the filler wire so you can put down more wire faster and make a smoother weld. Cold wire feed gives you more control over your heat input and is great for doing precision welding.

Weld Sequencing
Planning the order you weld stuff can help keep your metal from warping. For example, if you weld from the middle out or switch sides, you can control the heat and keep your metal from warping, especially on big pieces of sheet metal.
Peening
Peening is when you lightly hammer the weld bead to get rid of the stress left in the metal and keep it from cracking. This is good for thick metal and when you’re making stuff that has to hold a lot of weight.
Welding Symbols and Blueprint Reading
Learn the Symbols
You need to know what the welding symbols on blueprints mean. These symbols tell you what kind of weld to make, how big it should be, and how to weld it. You need to know the symbols to make sure you do the welds right and make the part the way you’re supposed to.
Read Blueprints
You need to know how to read blueprints to make sure you do your welds right. Blueprints tell you what to do and how big to make everything. They tell you how to make the part and what the part is supposed to look like. You need to know how to read blueprints to make sure you do the welds right and make the part the way you’re supposed to.
Technology in Sheet Metal Welding
Welding Automation
Think about using machines to help you weld. Robots can do the same thing over and over really well. They’re great at making sure everything is in the right spot every time. This helps you save money on people and make better welds.

Advanced Welding Machines
Get better welding machines with computers on them. These machines have buttons you can push to change the settings, screens that show you what’s going on, and can do more than one type of welding. They let you do more stuff and make your life easier.
Welding Software
Use computers to help you plan and practice your welds before you do them. This helps you see what could go wrong, make your welds better, and do a good job on your project.
Conclusion
Mastering sheet metal welding involves knowing the best ways to weld sheet metal and doing the right things to make your welding better. If you choose the right welding method, get your metal ready, and weld the right way, you can make good, strong welds in your projects. Don’t forget to be safe and check your welds to make sure they’re good. If you do all this stuff, you’ll get good at welding sheet metal.

