Are you struggling to understand the fundamentals of sheet metal bending? You’re not alone. This essential manufacturing process is crucial in producing parts and components used across various industries. The right bending techniques can ensure product quality and functionality, but the complexities can be daunting. Let’s break down the basics to help you get a clear understanding.
Sheet metal bending involves deforming metal along a straight axis to create specific shapes. Common methods include air bending, bottoming, and coining. Each method has its own advantages and applications. Understanding these processes, the equipment used, and the materials involved is essential for achieving high-quality bends.
Bending sheet metal is a crucial skill in the fabrication industry, impacting everything from automotive components to consumer electronics. By mastering the basics, you can ensure your projects meet both aesthetic and functional requirements. In this guide, we’ll explore different bending methods, the tools and materials involved, and key factors to consider for quality bending. Whether you’re new to the field or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive overview will provide valuable insights.
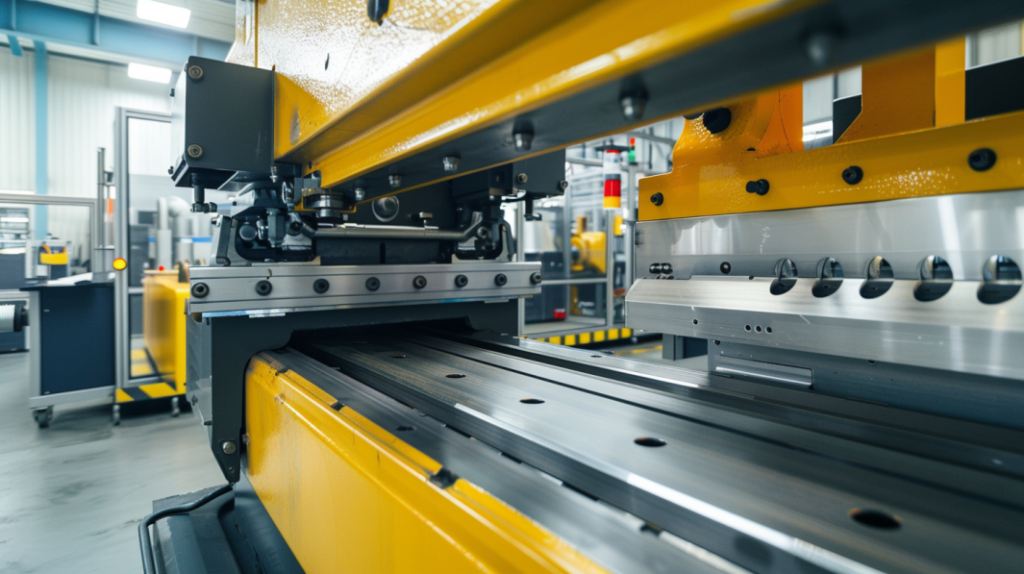

What is Bending Sheet Metal?
Bending sheet metal is the process of changing the shape of a piece of metal along a straight axis to make a specific shape. You typically do this with a press brake, which pushes the metal over a die. The goal is to make precise angles and shapes that meet your design requirements. People bend metal for all kinds of things, from making parts for cars to building stuff for the aerospace and consumer electronics industries.

What Are the Different Ways to Bend Sheet Metal?
- Air Bending:Air bending is great because it’s flexible and efficient. You put the sheet metal on a die, and then a punch comes down and bends the metal, but not all the way into the die. You can make a range of angles without changing the tooling. It’s cheap and versatile, which makes it great for lots of different things.

- Bottoming:Bottoming, or bottom pressing, is when you press the metal sheet all the way into the die. Bottoming gives you more precise angles and stronger bends than air bending, but you need different tooling to make different angles and work with different materials, which can be more expensive. People use bottoming when they need to be super accurate and consistent.

- Coining:Coining is a very precise way to bend metal. With coining, the punch and die come down and press completely into the metal with high pressure. This makes very accurate, repeatable bends with very little springback. People use coining when they need to make high-precision parts that have tight tolerances.

What Equipment Do You Need to Bend Sheet Metal?
Press Brakes
Press brakes are the main machines people use to bend sheet metal. They come in different types, including manual, hydraulic, and CNC (computer numerical control) models. CNC press brakes are super accurate and efficient. They make it easy to make complex bends and bend a lot of parts.
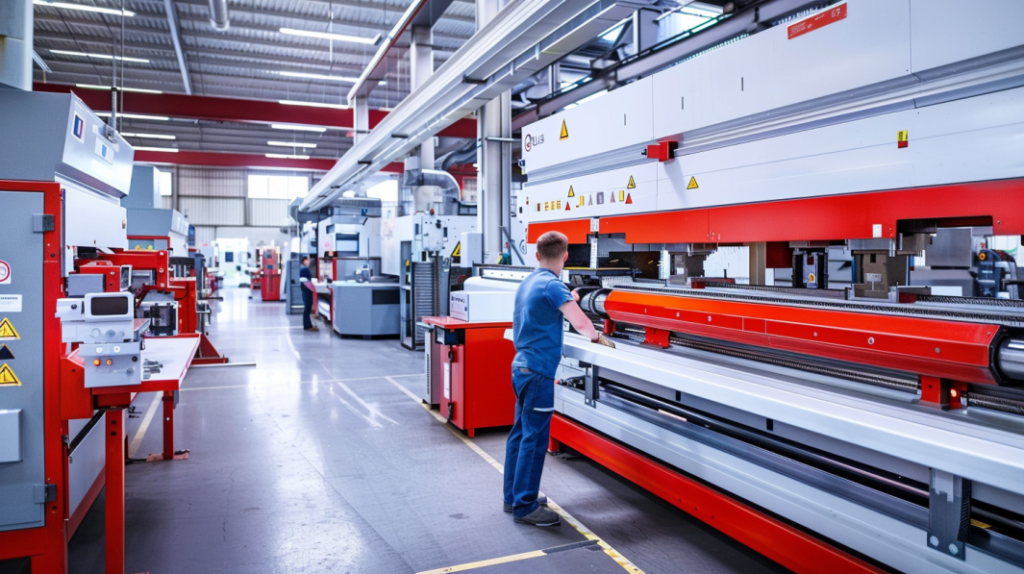

Bending Dies
Bending dies are critical tools in the bending process. They come in different shapes, like V-dies, U-dies, and custom profiles, to make different kinds of bends. The die you choose affects the radius of the bend, the angle of the bend, and how good the part looks when you’re done bending it.
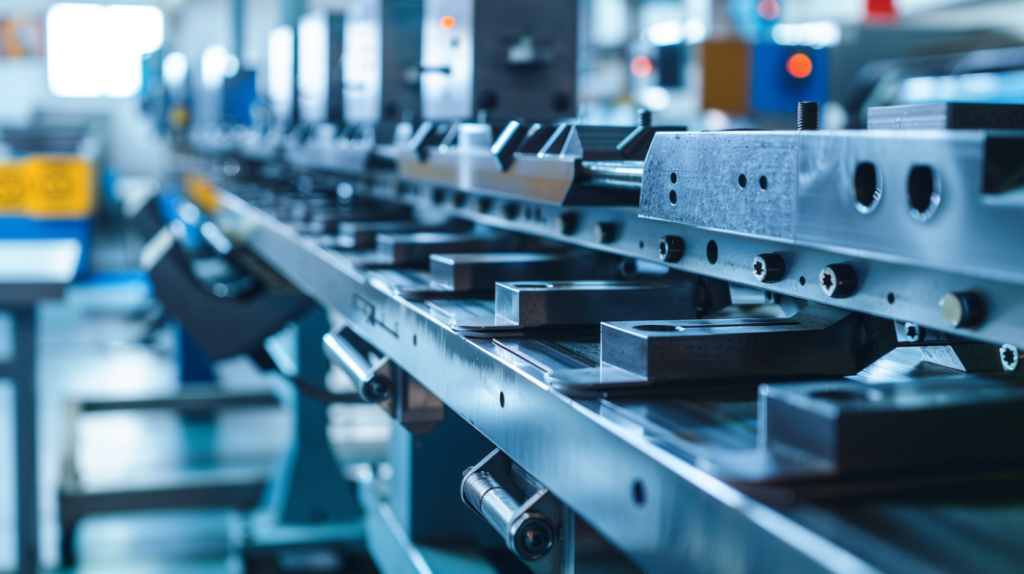

What Kind of Metal Can You Bend?
Different metals have different properties that make them good for bending. Here are some of the most common ones:
Aluminum
• Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, doesn’t corrode, and is easy to form.
• Common Alloys: People often use 5052, 6061, and 3003 because they bend really well.
• Applications: People use this metal for aerospace parts, car parts, consumer electronics, and stuff that looks good.
Steel
• Properties: Steel is strong, tough, and comes in lots of different grades.
• Common Grades: People use mild steel (A36), high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel, and cold-rolled steel.
• Applications: People use steel for building stuff, making things for factories, building cars, and making things that have to hold a lot of weight.
Stainless Steel
• Properties: Stainless steel doesn’t corrode, is strong, and has a lot of tensile strength.
• Common Grades: People use 304 and 316 stainless steel because they have great mechanical properties and are good at fighting corrosion.
• Applications: People use stainless steel for making medical devices, food processing equipment, things for boats, and stuff that looks pretty.
Copper
• Properties: Copper is super malleable and is a great conductor of heat and electricity.
• Common Alloys: People use pure copper and brass (a copper-zinc alloy).
• Applications: People use copper for making electrical stuff, plumbing, stuff that looks nice, and things that heat and cool your house.

Brass
• Properties: Brass doesn’t corrode, is easy to form, and looks good.
• Common Alloys: People make brass with different amounts of zinc and copper.
• Applications: People use brass for making musical instruments, stuff that holds doors shut, things you use to make water go away, and stuff that looks good.
Titanium
• Properties: Titanium is super strong for how light it is, doesn’t corrode, and is good for your body.
• Common Grades: People use grade 2 (which is pure) and grade 5 (which is an alloy called Ti-6Al-4V).
• Applications: People use titanium for making airplane parts, things to put in your body, stuff that makes cars go faster, and stuff that goes in the water.
Magnesium
• Properties: Magnesium is super light, strong for how light it is, and not super easy to form.
• Common Alloys: People use AZ31 and AZ61 because they bend well.
• Applications: People use magnesium for making airplane parts, car parts, and stuff that makes noise when you drop it.
Nickel Alloys
• Properties: Nickel alloys can handle high temperatures, don’t corrode, and are strong.
• Common Alloys: People use Inconel and Monel.
• Applications: People use nickel alloys for making airplane engines, stuff that makes chemicals, and things that go in the water.
Zinc
• Properties: Zinc melts at a low temperature, doesn’t corrode, and is easy to form.
• Common Applications: People use zinc to put a coating on steel so it doesn’t corrode, to make stuff with a mold, and to make little pieces of stuff.
What Affects the Quality of a Bend?
Bend Radius
The bend radius is important for the quality of the bend. If the radius is too small, the part might crack. If the radius is too big, the part might spring back. You have to choose the right bend radius based on the type of metal you’re bending.
Material Thickness and Type
Thicker metal is harder to bend and is more likely to crack. Different metals bend differently, too. For example, stainless steel is a lot stronger and less bendy than aluminum.
Tooling and Setup
You need to have the right tools and your machine set up right to make good bends. Using the right die and punch, making sure everything lines up, and setting the right stuff on your press brake all matter.
Springback
Springback is when the metal goes back a little bit to its original shape after you bend it. Springback happens differently with different metals and when you use different ways to bend the metal. To make the angles right, you have to make up for the springback.

What Are the Bending Techniques?
Manual Bending
Manual bending is when you use hand tools and simple machines to bend metal. It’s good for small projects and making one of something, but it’s not good for making a lot of things. People use things like hand brakes and hammers to bend metal by hand.
Automated Bending
Automated bending, especially with a CNC press brake, is super accurate and efficient. These machines use a computer to move stuff and bend metal really well without a lot of people helping. They’re great for making a lot of stuff and making stuff that has to be just right.
Fancy Bending Techniques
• Roll Bending: People use this to make big, round bends in pipes and tubes.
• Rotary Draw Bending: People use this to make pipes and tubes that have to be just right.
• Wipe Bending: People use this to make really tight bends and stuff that’s weird shapes.
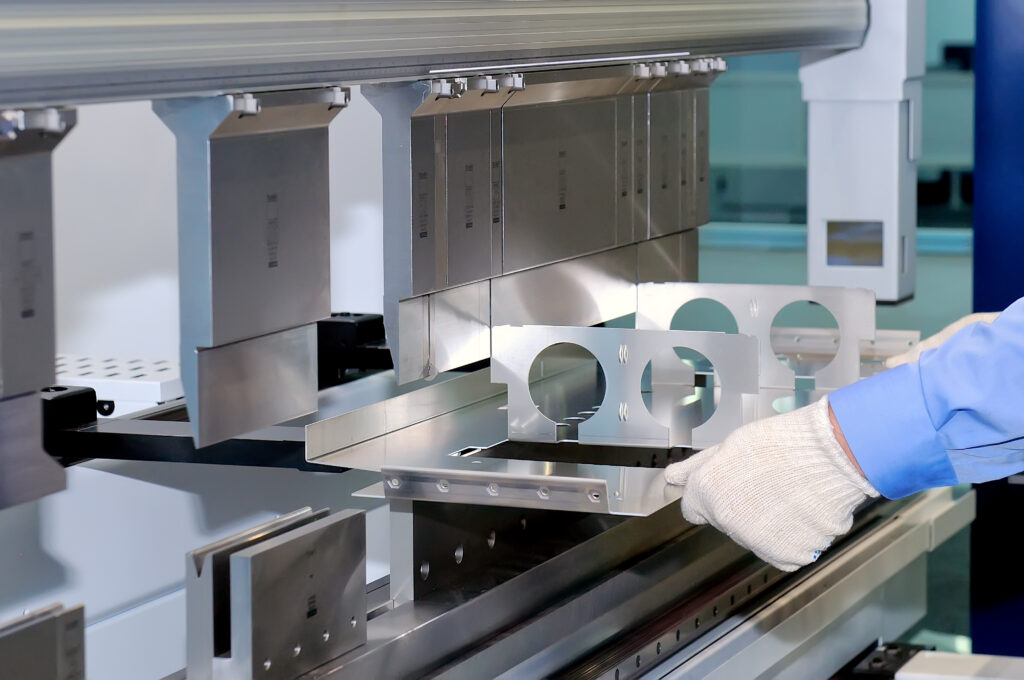

How Do You Design Something to Bend?
When you design something you want to bend, you need to make sure you do it right. Here’s how you can make sure you bend metal the right way:
• Make sure you have a drawing that shows what you want to bend.
• Think about how big you want the bend to be and what kind of metal you’re bending, so you don’t mess it up.
• Remember that the metal will go back a little bit, so you have to make the bend a little bigger to get the angle right.
• Don’t make designs that bend over holes or cuts. The metal will be weak, and your part might not work.

What Can Go Wrong When You Bend Metal?
Wrinkles and Cracks
Wrinkles happen when the metal gets squished too much, and cracks happen when the metal stretches too much. You can fix this by changing the bend radius, using the right tools, and picking the right metal.
Angles That Are Wrong
If the angles are wrong, you didn’t set up your machine right or you didn’t account for the metal moving back. You can fix this by making sure your press brake is set up right, using a back gauge, and thinking about the metal moving back when you make the first bend.
Stuff that Doesn’t Fit Together
If the parts don’t fit together, you can’t put them together. You can fix this by making the bends right, making sure everything lines up, and checking the quality of your parts.
How to Fix Bending Problems ?
Figure Out What’s Wrong
Look at the part and how you’re bending it to figure out what’s not working. Check the tools, how the machine’s set up, and if the metal is good.
Change the Way You’re Bending
Fix the problem by changing how you’re bending the metal. You might have to change the die, adjust the press brake, or use a different kind of metal.
Check Your Work
Look at the parts you’re making to make sure they’re good. Check the angles and how the part fits together using tools like calipers and angle finders.

How to Stay Safe When You Bend Metal ?
- Wear the Right Stuff: Always wear gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toed shoes.
- Keep the Machine Safe: Make sure all the safety stuff on the machine works right.
- Know What You’re Doing: People using the machine should know how to make stuff and watch out for problems.
- Keep Your Area Safe: Make sure your workspace is clean and doesn’t have stufflying around that could cause problems.
Conclusion
Knowing how to bend sheet metal helps you make good parts. By understanding the different ways you can bend metal, using the right tools, and thinking about what kind of metal you’re bending, you can make sure your parts are perfect and look the way you want. Whether you’re making one part or a lot, these basics will help you make your parts better and make sure your projects are the best they can be. If you also think about staying safe and how people use the parts you’re making, you’ll be able to bend metal the right way every time.

