Struggling to decide between galvanneal and galvanized steel for your next project? It can be tough. They both have their own unique benefits. Understanding the differences between the two in the world of steel coatings can save you time, money, and a few headaches.
Both galvanneal and galvanized steel offer excellent protection against corrosion. However, they have different purposes. Galvanized steel is known for its shiny finish and its affordability. Galvanneal steel is known for its superior paintability and weldability. Knowing what you need for your particular project will help you make the right choice.
Let’s take a closer look at both of these materials. By understanding their processes, their advantages, and their typical applications, you’ll have a better idea of which type of steel will work best for your project. Whether you’re working in the automotive industry, the construction industry, or the manufacturing industry, this guide will help you make a more informed decision.
What is Galvanization?
Galvanizing is the process of coating steel with a protective layer of zinc to prevent rust. The zinc barrier acts as a sacrificial anode so that it will corrode before the steel will if it is exposed. Not only does this make the steel last longer, but it also makes the steel look better, which is why it is used for so many different things. People like galvanized steel because it is strong, it lasts a long time, and it can be used for a variety of things.

How Does Galvanization Offer Protection?
The way galvanizing works is the zinc will corrode before the steel will, so even if the zinc coating gets a little scratched, the steel underneath is still protected from rusting.
To be successful, galvanizing requires good pretreatment and good post-treatment. You have to clean the steel really well and remove any impurities. You have to pickle the steel to get it ready to have the zinc stick to it. You have to flux the steel so the zinc will stick to it. You have to check the coating thickness and make sure it’s consistent to get the best possible life out of your galvanized steel.
The Galvanizing Process
- Clean: Clean the steel to remove all the impurities like grease, oil, and wax. Dip the steel in a degreasing solution to get it clean.
- Pickle: Dip the steel in a hot diluted solution of sulfuric acid to prepare the steel for the zinc to stick to it.
- Flux: Dip the steel in a salt solution such as zinc ammonium chloride to help the zinc stick to the steel.
- Galvanize: Dip the clean, pickled, and fluxed steel in molten zinc at 850°F. The zinc will bond to the steel at the molecular level.
- Post Process: Inspect the steel for coating thickness and consistency. Use air knives to control the coating thickness. You can also paint or do other processes to the steel.

Advantages of Galvanization (Hot-Dip Galvanization)
• Low Maintenance and Low Long-Term Cost: Costs less up front than other coatings like painting or electroplating. Costs less to maintain over time, which saves you money in the long run.
• Long Life: Galvanized steel will last at least 50 years in rural areas and 25 years in urban areas.
• Durable and Strong Coating: The zinc coating ensures the steel will be durable and strong and not be damaged mechanically. The process is reliable and allows for consistent coating specifications.
• Automatic Protection: The zinc coating is a sacrificial or cathodic layer that protects the steel from the environment. You don’t have to touch it up like you do with organic coatings.
The Galvannealing Process
Galvannealing is the process of galvanizing steel and then putting it in an oven at 1050°F. When it’s in the oven, the iron in the steel migrates into the zinc coating, forming a zinc-iron alloy. This alloy allows paint to stick to it better and makes the steel easier to weld. It has a matte gray finish that doesn’t scratch and chip as easily as regular galvanized steel.

Advantages of Galvannealing
• Better Formability and Weldability: Great for spot welding and for forming complex shapes.
• Excellent Paintability: The surface is better for paint to stick to than regular galvanized parts.
• Less Likely to Rust: It’s very resistant to rusting but is a little less strong than regular galvanized steel.
• Strong: It’s stronger and harder to damage than regular galvanized steel.
Types of Galvanizations
• Hot-Dip Galvanizing: The most common method where steel is dipped in molten zinc at 860°F. This process creates a metallurgical bond and a spangle pattern on the surface.
• Electro-Galvanizing: Zinc ions are applied using an electrical current in an electrolyte solution. This process creates a very uniform coating thickness.
• Pre-Galvanizing: Similar to hot-dip, but this process is done at the steel mill. This allows steel coils to be galvanized quickly.
• Thermal Spray (Metallizing): After the part is blasted with grit to clean it, the part is sprayed with semi-molten zinc using an arc or a plasma heat source.
• Sherardizing: The steel part is put into a rotating drum with zinc dust and sand. The drum is heated up so that the zinc diffuses into the steel.
Benefits of Galvanized Sheet Metal
- Corrosion-Resistant: Offers excellent protection against rust and corrosion.
- Long Lifespan: Lasts up to 50 years in rural areas and 20-25 years in urban settings.
- Durable and Tough: Withstands significant wear and tear, ideal for harsh environments.
- Low Maintenance: Requires minimal upkeep, reducing long-term costs.
- Cost-Effective: Affordable initial cost with high-performance coating.
- Complete Coverage: Ensures uniform protection, including edges and corners.
- Quick Turnaround Time: Fast galvanization process, often completed within 24 hours.
- Environmental Benefits: Recyclable and reduces the need for frequent replacements.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Distinctive, shiny appearance suitable for architectural uses.
- Versatile: Applicable in automotive, construction, agriculture, and energy sectors.
- Reliable Performance: Consistent and predictable coating quality.
Uses and Applications of Galvanized Sheet Metal
Automotive Industry
Galvanized steel is used a lot in the automotive industry because it doesn’t rust and is strong. They use it for car bodies, frames, and bicycle parts because the steel is strong and looks good. Many cars come with warranties against rust because companies know people don’t want to buy a car that is going to rust.
Telecommunication Industry
In the telecommunication industry, they use galvanized steel for phone wiring and equipment boxes because it doesn’t rust and doesn’t need to be maintained. It’s great for putting phone lines up in harsh outdoor environments because they don’t have to worry about them rusting.
Electric Equipment and Appliances
A lot of electrical appliances have cases made from galvanized steel. It’s used on the outside of electrical appliances to protect them from rust, and it’s used on the inside to make the appliance last longer and be safer.
Construction Industry
Galvanized steel is used a lot in construction because it doesn’t rust and is strong. They use it for things like balconies, porches, stairs, ladders, walkways, fences, and roofs.
Energy Sector
Galvanized steel is used in the energy sector for electrical wires and solar panels because it doesn’t need to be maintained and it doesn’t rust. It’s good for making energy in a way that doesn’t hurt the environment.
Agriculture Sector
In agriculture, they use galvanized steel a lot because they put a lot of equipment outside in the weather. They don’t want it to rust, so they use galvanized steel to make sure their equipment lasts for a long time.
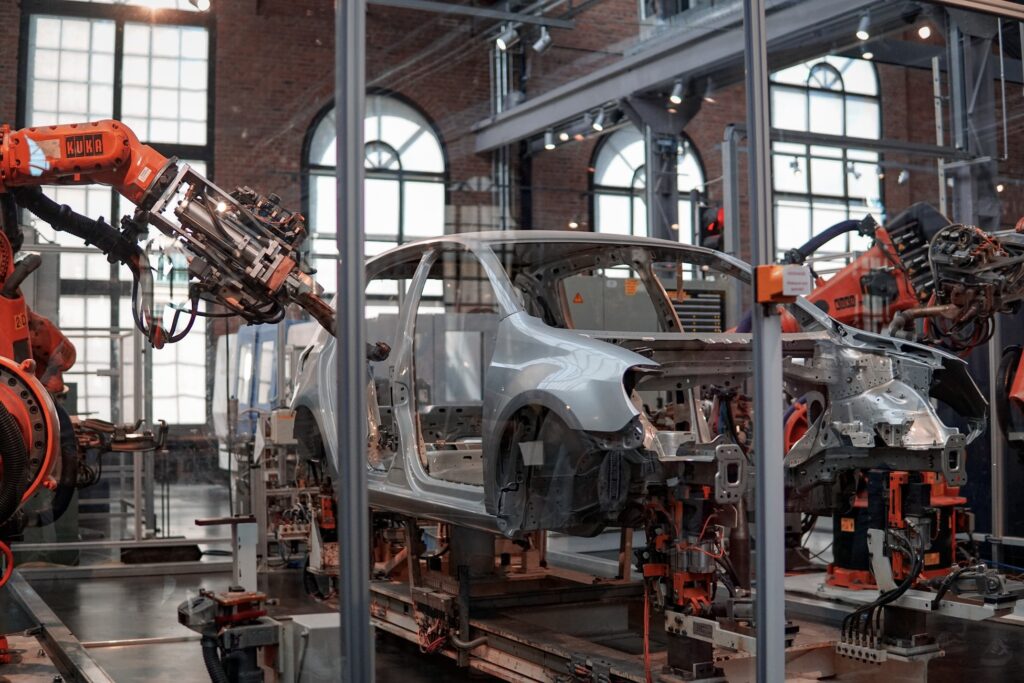

Benefits of Galvanneal Sheet Metal
- Superior Paintability: Enhanced surface for better paint adhesion.
- Enhanced Weldability: Ideal for spot welding and other welding processes.
- Improved Corrosion Resistance: High resistance to rust and corrosion.
- High Formability: Easily shaped into complex geometries without losing strength.
- Durable and Tough: Resistant to mechanical damage and wear.
- Consistent Coating: Uniform protection across the entire surface.
- Superior Surface Quality: Matte gray finish that resists scratching and chipping.
- Environmentally Friendly: Recyclable and promotes sustainability.
- Wide Range of Applications: Used in automotive, waste disposal, and marine industries.
- High Tensile Strength: Suitable for applications requiring strong, durable materials.
- Reliable Performance: Consistent quality for critical applications.
- Competitive Pricing: High value for money despite slightly higher initial costs.
Uses and Applications of Galvanneal Steel Products
Automotive Industry
Automobile companies like Honda, Toyota, and Ford use galvannealed steel for making car bodies. They like to use it because it’s easy to weld, easy to form, and paint sticks to it really well. They use it for making high-quality car parts.
Waste Disposal
Galvannealed steel is used for making really tough trash systems like trash chutes and linen chutes. It’s very strong and you don’t have to do much to keep it in good shape.
Marine Applications
Galvannealed steel is used in boats because it’s strong and you can weld it. Boats have to be strong and last a long time in the water, so you need something that won’t rust and will last.
Forming and Deep Drawing
Galvannealed steel is used for making things that have to be formed and deep drawn. It’s easy to use to make complex shapes and parts.
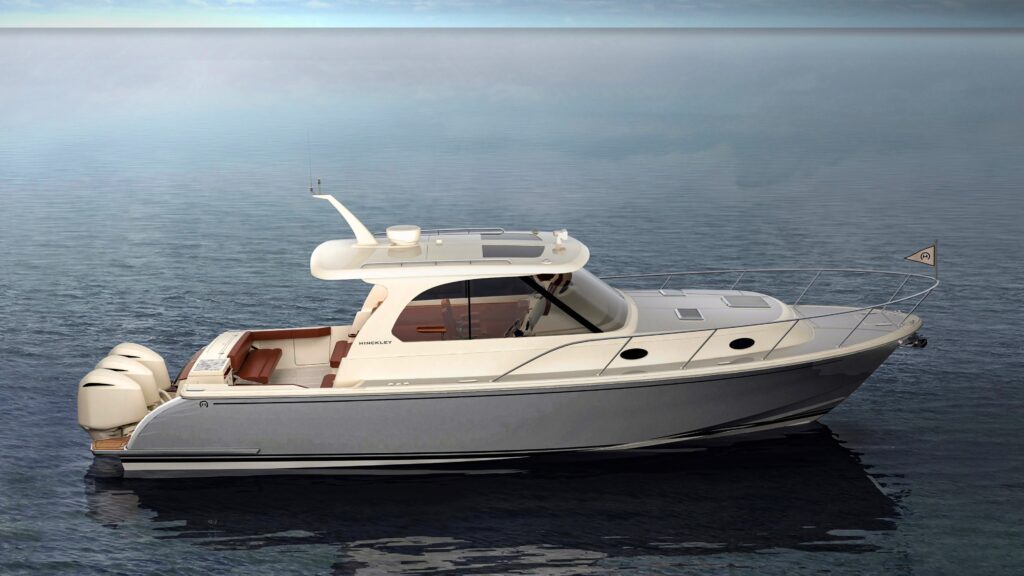

Similarities Between Galvanneal vs. Galvanized Steel
Properties
Both galvanized steel and galvannealed steel don’t rust. They’re very strong and can be used for all kinds of things. Galvannealed steel is a little better at not rusting than galvanized steel.
Process
Both materials are coated with zinc using the hot-dip galvanization process. Galvannealed steel goes through an additional process to make it, which makes it different than galvanized steel.
Differences Between Galvanneal vs. Galvanized Steel
Coating
• Galvanized Steel: A primarily zinc coating with a little bit of iron mixed in.
• Galvanneal Steel: Has multiple layers (zeta, delta, gamma) because of the way it’s made, which makes it harder and stronger.
Appearance
• Galvanized Steel: Looks shiny and metallic.
• Galvanneal Steel: Has a dull gray matte finish because of the iron in the coating.
Weldability
• Galvanized Steel: Not as easy to weld.
• Galvanneal Steel: Easier to weld, especially for spot welding, because of the iron in the coating.
Paintability
• Galvanized Steel: Paint sticks to it really well without having to sand it.
• Galvanneal Steel: Paint sticks to it really well, even better than galvanized steel, so it’s good for painted applications.
Formability
• Galvanized Steel: You can machine it a little easier because the coating is softer.
• Galvanneal Steel: You can form it a little easier because it goes through an annealing process, which makes it easier to form complex shapes.
Cost
• Galvanized Steel: Costs less because it doesn’t go through the extra annealing process.
• Galvanneal Steel: Costs a little more because it has to go through the extra annealing process, but it works better for certain things.
| Characteristic | Galvanneal Steel | Galvanized Steel |
| Coating | Three zinc-iron layers | One zinc layer |
| Appearance | Dull gray matte | Shiny metallic |
| Weldability | Ideal for spot welding | Less weldable |
| Paintability | Higher paintability | High paintability |
| Formability | Higher formability | High formability |
| Corrosion Performance | Higher corrosion resistance | High corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost | High cost |
Choose the Right Steel for Your Project
Choosing between galvanneal and galvanized steel can be tough because they both have their own unique properties. I’ve given you the rundown on both types of zinc coating processes and what they’re good for, but you still might need some help picking the right one for your project.
We’ve got a team of experts at Premium Rapid & Mold in sheet metal fabrication who can help you pick the right material. We do sheet metal fabrication for people all over the world. Our team is committed to making sure your parts meet the highest standards. We can save you up to 30% on your project and get it done quickly. Upload your design file now and we’ll get back to you with a quote and DFM analysis in 12 hours.
FAQs
Is galvanized and stainless steel the same?
No, galvanized steel and stainless steel are different. Galvanized steel gets its protective coating by dipping into hot zinc, while stainless steel has the protective part built into the steel, which makes it more expensive and stronger.
Can galvanized steel and stainless steel be used together?
No, you shouldn’t use galvanized steel with stainless steel. The two materials will interact and cause the galvanized steel to rust faster.
Is galvanized steel stronger than regular steel?
Yes, galvanized steel is stronger than regular steel because the zinc coating on the steel makes it stronger and last longer.

