Are you overwhelmed by all the different sheet metal finishes available? You’re not alone. The right finish is critical for the appearance and durability of your parts. It can improve corrosion resistance, enhance the appearance, and make your parts last longer. But there are a lot of finishes to choose from. Let’s take a look at all the different types to help you make the right choice.
There are a lot of different types of sheet metal finishes, each with its own benefits for different applications. These include standard finish, bead blasting, brushing, anodizing (Type II, and Type III), powder coating, chromate conversion coating, black oxide, electropolishing, zinc plating, galvanizing, passivation, tinning, nickel plating, phosphate coating, PVD coating, CED coating, and powder metallizing. Knowing your options will help you choose the right finish.
Picking the right sheet metal finish is an important step in making sure your parts look good and perform well. From preventing corrosion to making things look good, each finish has its own benefits. In this guide, we’ll look at the most common finishes and talk about the benefits and applications of each. Whether you’re in the automotive, aerospace, or consumer electronics industry, knowing your finishes will help you choose the right finish for your projects.
What Are the Benefits of Each Sheet Metal Finish?
1.Standard Finish
The standard finish is the most basic sheet metal finish. You don’t do anything to it. You cut it, you form it, you’re done. This is the cheapest finish you can get. This finish is great for parts that aren’t going to be exposed to harsh conditions. You use it for internal components, structural parts, things like that where you don’t care what it looks like.
2.Bead Blasting
Bead blasting uses glass beads to create a uniform matte or satin surface. It’s great for deburring edges, removing tool marks, and creating a surface that has a little bit of grip to it. You can also use bead blasting to prepare surfaces for coatings and to create an aesthetic finish on consumer goods. For example, bead blasting is great for automotive and aerospace components that need a consistent surface texture.

3.Brushing
Brushing is a process where you polish the material with grit to create a unidirectional satin finish. It makes the part look great and removes imperfections created by machining. You see brushed finishes on consumer electronics and kitchen appliances. Brushed finishes are also popular on decorative panels and visible parts because they look really nice and modern.

4.Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that creates a protective oxide layer on the surface of the metal. There are two main types:
• Type II: This is a decorative and protective finish.
• Type III (Hardcoat): This is a hard, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant finish.
Anodizing makes the part tougher and can be dyed different colors. You see anodizing on things like electronics casings, aerospace parts, and marine stuff.

5.Powder Coating
Powder coating is where you spray a polymer on the part and then bake it in an oven. This is a very tough finish that looks good and is weather and corrosion-resistant. People use powder coating on things like outdoor furniture, automotive parts, and industrial stuff because it’s tough and looks nice.
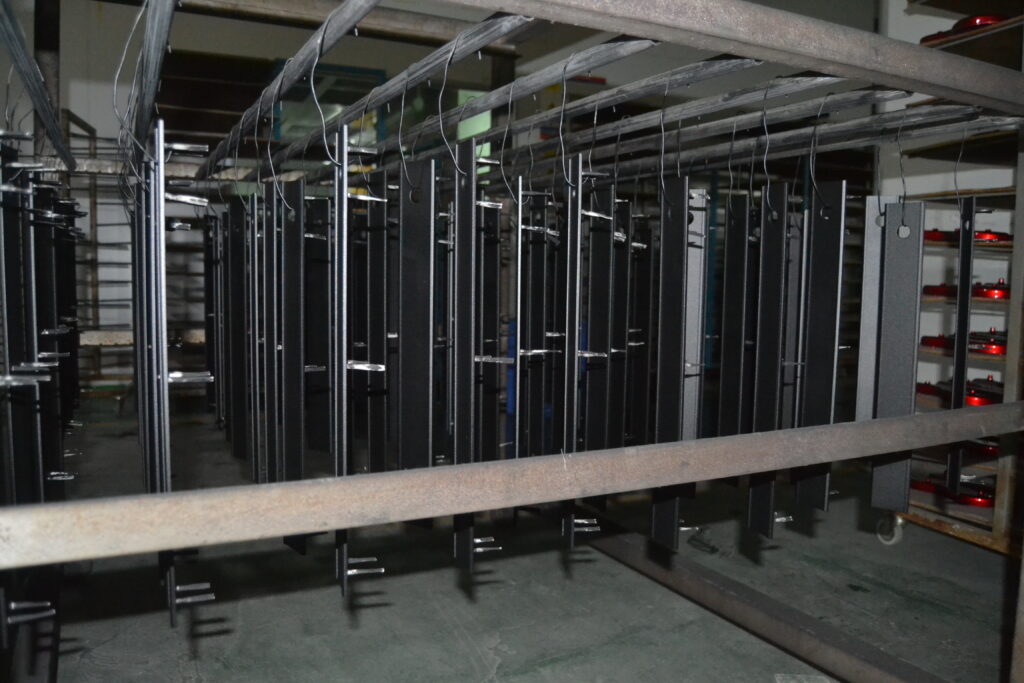

6.Chromate Conversion Coating
Chromate conversion coating is when you dip the metal in a chemical bath to create a layer of chromate on the surface. This finish protects against corrosion, helps paint stick to the part, and allows electricity to flow through the part. People use chromate conversion coating on things like aerospace components, electronic enclosures, and fasteners.
7.Black Oxide
Black oxide is a chemical conversion coating for steel that’s used to improve corrosion resistance and reduce glare. People use black oxide on things like guns, tools, and machine parts because it’s tough and not shiny.

8.Electropolishing
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that makes the metal smooth and shiny. It also makes the part more resistant to corrosion, cleaner, and shinier. You see electropolishing on stuff like medical devices, food processing equipment, and pharmaceutical machinery.

9.Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is when you electroplate zinc onto the part to keep it from corroding. This is a cheap finish that protects the part from rust. People use zinc plating on things like fasteners, automotive parts, and hardware.

10.Galvanizing
Galvanizing is when you coat steel with a layer of zinc to keep it from corroding. There are two types:
• Hot-Dip Galvanizing: You dip the part in molten zinc.
• Electro-Galvanizing: You electroplate the part.
People use galvanizing on outdoor structures, automotive frames, and construction parts because it’s tough and will last a long time.

11.Passivation
Passivation chemically treats stainless steel to remove free iron and make it more resistant to corrosion. This is important because it keeps the metal from rusting and looking bad. People use passivated parts in medical instruments, food processing equipment, and chemical containers.
12.Tinning
Tinning is when you coat the part with a thin layer of tin to keep it from corroding and make it easier to solder to. People use tinning on things like food cans, electrical components, and bearings because it’s safe and it conducts electricity.
13.Nickel Plating
Nickel plating is when you put a layer of nickel on the part to make it look nice and to keep it from corroding. This process also makes the part harder, more resistant to wear, and more resistant to corrosion. People use nickel plating on things like jewelry, electronic components, and automotive parts.
14.Phosphate Coating
Phosphate coating is when you put a layer of phosphate on the part to help paint stick to it and to keep it from corroding. People use phosphate coating on things like automotive parts, industrial machinery, and guns because it creates a nice surface for paint to stick to.
15.PVD Coating (Physical Vapor Deposition)
PVD coating is when you put a thin film of material on the part in a vacuum chamber to make it hard, tough, and pretty. This is a fancy process that makes the part really resistant to wear. People use PVD coating on things like cutting tools, medical devices, and decorative hardware.
16.CED Coating (Cathodic Electrodeposition)
CED coating is when you put a primer on the part using an electrochemical process that makes the finish even and resistant to corrosion. People use CED coating on things like automotive bodies, industrial machinery, and appliances because it protects the part really well.
17.Powder Metallizing
Powder metallizing is when you spray molten metal on the part to make it more resistant to wear and corrosion and to let you coat complex shapes. People use powder metallizing on things like aerospace parts, automotive components, and industrial machinery because it makes the part tough and lets you coat it in different ways.
How to Choose the Right Sheet Metal Finish for Your Project?
Choosing the right sheet metal finish depends on what you’re making, where it’s going to be, and how you want it to look. Here are some things to think about when you’re choosing a finish:

Where It’s Going
Think about what it’s going to be exposed to. If it’s going outside, you might want something like powder coating, galvanizing, or anodizing that will keep it from rusting.
How You Want It to Look
If it’s something you’ll see, you might want a finish that looks nice like brushing, anodizing, or powder coating. These finishes will make your part look sleek and modern while keeping it protected.
How Much It’s Going to Get Beat Up
If it’s going to get beat up a lot or rubbed against other things, you might want a finish that’s really tough. Anodizing (Type III Hardcoat), nickel plating, and PVD coating are good finishes for parts that are going to get a lot of wear and tear.
How Much You Want to Spend
You have to balance how much a finish costs with what you get. Standard finishes and zinc plating are cheap, but finishes like PVD coating and powder metallizing are more expensive. They do cool things, but they cost more money.
What You’re Making
Different industries need different finishes. For example, medical devices need electropolishing to keep them clean and corrosion-resistant, while automotive parts might need powder coating or galvanizing to keep them looking good and lasting a long time.
Conclusion
Picking the right sheet metal finish is important to make sure your part works well, lasts a long time, and looks good. By knowing what each finish does and where you can use it, you’ll be able to pick the right finish for your project. Whether you need to keep it from rusting, make it look good, or make it last forever, there’s a sheet metal finish that’s perfect for your project.

